VS IntelliSense#
Code completion, also known as autocomplete or auto-suggestion, is a feature that automatically suggests possible completions for partially typed code. When you start typing a variable name, function, or method, the editor presents a list of relevant options that match what you’ve typed so far.
IntelliSense is Microsoft’s implementation of intelligent code completion in Visual Studio Code. IntelliSense works with many programming languages including Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, C++, and more. For Python specifically, it provides completions, signature help, quick info, and code coloring.
To use IntelliSense effectively in VS Code, simply start typing and press Ctrl+Space to trigger suggestions manually, or let it appear automatically as you code.
Part 1: Completions#
Completions appear as statements, identifiers, and other words that can be appropriately entered at the current location in the editor. Intellisense populates the list of options based on context and filters incorrect or distracting items. Completions are often triggered by entering different statements (such as import) and operators (including a period).
When a completion list is open, you can search for the completion you want by using the arrow keys, the mouse, or by continuing to type. As you type more letters, the list is further filtered to show likely completions. You can also use shortcuts such as:
Type letters that aren’t at the start of the name, such as ‘parse’ to find ‘argparse’
Type only letters that are at the start of words, such as ‘abc’ to find ‘AbstractBaseClass’ or ‘air’ to find ‘as_integer_ratio’
Skip letters, such as ‘b64’ to find ‘base64’
Member completions appear automatically when you type a period after a variable or value, along with the methods and attributes of the potential types. If a variable can be more than one type, the list includes all possibilities from all types. Extra information is shown to indicate which types support each completion. When all possible types support a completion, no annotation is shown.
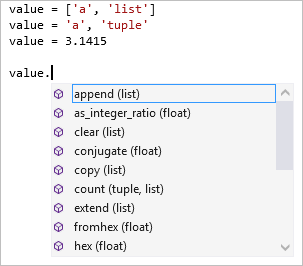
The import and from ... import statements display a list of modules that can be imported. The from … import statement produces a list that includes members that can be imported from the specified module.
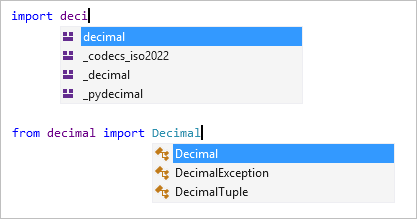
Pressing Tab or Enter will insert the selected member.
\(\text{Task 2.1:}\) Try completions
Try completions by importing numpy and creating an array with the linspace function from 4 to 10.
Use completions to insert numpy and a function of numpy to create an array.
import numpy as np
array1 = np.linspace(4, 10, 10)
Solution:


Part 2: Signature help#
When writing code that calls a function, signature help appears when you type the opening parenthesis (. It displays available documentation and parameter information. You can access signature help with the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Shift+Space inside a function call. The information displayed depends on the documentation strings in the function’s source code, but includes any default values.
An example is shown below:

The Quick Info/Hover IntelliSense feature provides the same information when hoovering over a function.
\(\text{Task 2.2:}\) Try signature help
Try signature to replace world with MUDE.
text = "hello world"
newtext = text.replace("world", "MUDE")
Solution:

By Tom van Woudenberg, Delft University of Technology. CC BY 4.0, more info on the Credits page of Workbook.
